Laxatives and Purgatives as natural drugs helps in constipation
 |
| Laxatives and Purgatives |
Laxative word is formed from Latin word Laxare which means to loosen.
| Detoxyn supports natural body cleansing processes |
Definition:-
Laxatives are the drugs that helps in loose of bowels (intestine) and promote defecation (push out excreta from the body through anus).
In other words, those natural drugs producing , increasing and hastening intestinal evacuation.विरेचक या आरेचक (Laxatives या purgatives या aperients) ऐसे खाद्यपदार्थ, यौगिक या दवाओं क कहा जाता है जिनके सेवन से मलत्याग में आसानी होती है। इनके उपयोग से मलाशय की सफाई करने में आसानी होती है।
Examples :- Aloe, Rhubarb, Senna, Caster oil, Isapghula etc.
Mechanism of action:-
Laxatives may be either bulk forming, irritant or emollient depending upon the chemical nature of the active constituent. They are mostly given to patients prior to diagnostic procedure or surgery.
▪Laxatives:- Helps in the elimination of soft formed stools. They are also known as mild purgatives. Examples are :- senna, isapghol, liquid paraffin etc.
Types of Laxatives
Depending upon the intensities of the drug effects, laxatives are categories as follows:-▪Laxatives:- Helps in the elimination of soft formed stools. They are also known as mild purgatives. Examples are :- senna, isapghol, liquid paraffin etc.
▪Purgatives:- It helps in releasing more fluid from intestine. Examples:- caster Oil, aloe, sagrada, rhubarb etc.
▪Drastics or irritants:- These drugs acts intensely by irritating the mucous membrane of the intestine. Examples :- jalap, podophyllum etc.
▪Hydrogogues:- It produce extreme fluid motions. Examples:- croton oil, colocynth.
▪Hydrogogues:- It produce extreme fluid motions. Examples:- croton oil, colocynth.
 |
| Laxative Table |
ALOE VERA
A) Geographical Distribution:-
Aloe is indigenous to Africa, now available in West indies and Europe. It is cultivated throughout India.
 |
| Aloe Vera |
B) Physical appearance:-
Colour- Dark greenish brown,
Odour- Characteristic ,
Taste – bitter and nauseating
C) Solubility:-
It is entirely soluble in 60% alcohol and partly soluble in water.
D) Identification test:-
•Modified Borntrager’s test:-
Aloe sample + 5% FeCl3 + 2ml dil HCl. Boil for 05 minutes in waterbath. Cool and shake with benzene. Seprate benzene layer and add equal amount of dil ammonia. Result pink-red colour ppt formed.
Aq sol. Of sample + few drops of CuSO4 + 0.5 grm NaCl + 90% alcohol. Result wine red color appears.
E) Uses:-
It is used as irritant purgative. Now a days aloe gel is used in cosmetics as a protective i.e, in anti wrinkle creams , hair shampoo. Externally, it is applied for painful inflammation.
● F) Chemical constituents:-
 |
| Barbaloin & Aloe-emodin |
RHUBARB
A) Geographical Distribution:-
It is collected and cultivated in China, India, Tibet, and European countries. In India it is cultivated in higher altitudes areas like Kashmir, Himachal and Assam.
Odour- fragrant,
Taste – bitter and astringent,
Size & shape – Rhizomes are sub-cylindrical, barrel-shaped, conical pieces. 2 to 20 cm in length and 1.5 to 2 cm in diameter.
C) Adulterants :-
Rhapontic rhubarb, a Chinese rhubarb is used as an adulterant.
•By addition of ammonia, it acquires pink colour.
D) Identification test:-
•By addition of ammonia, it acquires pink colour. •Borntrager’s test :- Rhubarb sample + 2ml dil HCl. Boil for 05 minutes in waterbath. Cool and shake with benzene. Separate benzene layer and add equal amount of dil ammonia. Result pink-red color ppt formed.
•Under UV radiation Rheum-emodi gives brown coloration.
E) Uses:-
Rhubarb is a mild purgative. Its action is like that of cascara aloe.
 |
| Rhubarb plant |
 |
| Rhubarb Rhizome |
It is collected and cultivated in tropical and sub tropical regions. India is the second largest producer of castor seeds around 2.8 lakhs tons per annum. Andhra Pradesh, Gujrat and Karnataka are largely producing castor seeds in India.
B) Physical appearance:-
 |
| Castor plant |
Color- Pale yellow,
Odor- Nauseating,
Taste – Nauseating.
C) Solubility :-
It is soluble in alcohol, miscible in chloroform, ether, glacial acetic acid and petroleum ether.
•An equal volume of alcohol is added to castor oil. Clear liquid is obtained.
D) Identification test:-
•It mixes with half its volume of light petroleum ether and partially soluble in its 2 volumes.•An equal volume of alcohol is added to castor oil. Clear liquid is obtained.
E) Uses:-
Castor oil is used as cathartic. It is also used as lubrication agent, it is also used in paints , enamel, varnishes, grease and many other Castor oil is a common base for many cosmetics products like hair oil and hair fixers.
F) Chemical constituents:-
 |
| Castor seeds |
- Stearic acid - CH3(CH2)16COOH or C18H36O2
- Linoleic Acid - C18H32O2
- Ricinoleic acid - C18H34O3
ISPAGHULA
A)Geographical Distribution:-
It is largely cultivated in Gujarat, Punjab and south Rajasthan. Around 30 thousand hectares of area is said to be under cultivation for the drug in India.
B) Physical appearance:-
 |
| Plantago Ovata forskal |
Odour- None
Taste – Mucilaginous
Size and shape- 10 to 35 mm in length and 1 to 1.75 mm in width,
it is ovate cymbiform. Seeds are hard, transparent and smooth.
C) Adulterants :-
The isapgol seeds are adulterated with the seeds of plant known as Plantago lanceolata.
D) Identification test:-
•Add few drops of Chinese-ink on dried seeds of Isapghula, mucilage shows transparent, spherically dilated fragments on black background.•Add few drops of Thionine test solution, wait for 10 minutes, wash with alcohol, mucilage turns violet-red.
E) Uses:-
 |
| Isapghula seeds |
Isapghula are used as demulcent, laxative, emollient and in the treatment of chronic constipation. It is also used as stabilizer in the ice-cream factory.
F) Chemical constituents :-
 |
| Isapghula chemical constituents |
SENNA
A)Geographical Distribution:-
Indian Senna is cultivated and collected in Tinnevelly, Madurai and Ramnathpuram district of Tamil Nadu. Other states which also cultivate senna are Gujarat, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh.
Colour- Leaves are yellowish green
Odour- Slight, Taste – Mucilaginous-bitter and characteristics
Size and shape- 7 to 8 mm width, 25 to 60mm length. Leaves are lanceolate, entire , apex is acute with spine at the top, leaflet bases are asymmetrical with transverse lines, more prominent, while trichomes are present on both the surfaces.
Pods & Seeds:-
Colour- Pale green /brown
Odour- None
Taste – Slight
Size and shape- 4 to 5 cms and 2 to 2.5 width, Pods are flat , thin ,broadly oblong, seeds are about six in number , obovate in shape , blunt at hilum end.
Mostly Indian Senna is adulterated with Italian senna, Arabian senna and Palthe senna .
D) Identification test:- Borntrager test
E) Uses:-
Senna is an irritant purgative due to the presence of anthraquinone derivatives. Its major disadvantage is that it causes gripping, but it is overcome by admixing with carminatives.
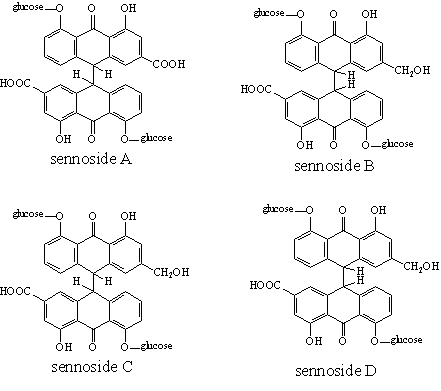
F) Chemical constituents:-
Final words:-
Laxatives as natural drugs are really helpful in constipation whether it is chronic or mild. These days it has been given as allopathic , Ayurvedic or as herbal treatment. Patients has been advised to consult with doctors before taking any kind of laxative drugs.
| Detoxyn supports natural body cleaning process |











0 Comments
If you have any doubts, please do share on the website in comment section.